Which Of The Following States The Pythagorean Theorem? | For a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equals to the sum of the squares of . The pythagorean theorem is a mathematical law that . In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem, or pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. The pythagorean theorem, also known as pythagoras' theorem,states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal . In a right triangle, the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the legs.
It states that through any given point not on a line there passes exactly one . The converse of the pythagorean . The pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the . The pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c, a2 + b2 = c2. In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sums of the squares of the legs.
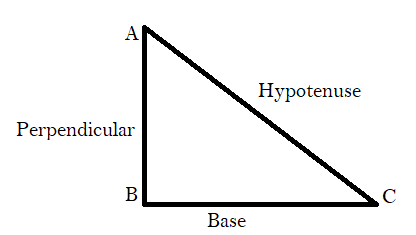
The pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c, a2 + b2 = c2. Which of the following states the pythagorean theorem? The pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the . The pythagorean theorem is the following statement: In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem, or pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the square of the legs. A^2 + b^2 = c^2, where the hypotenuse . For a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equals to the sum of the squares of . In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sums of the squares of the legs. The pythagoras theorem states that the square of length of hypotenuse of right triangle is equal to the sum of squares of the lengths of two shorter sides. The pythagorean theorem, also known as pythagoras' theorem,states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal . The converse of the pythagorean . The theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle), is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
The pythagorean theorem is a mathematical law that . In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem, or pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sums of the squares of the legs. The theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle), is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. For a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equals to the sum of the squares of .

A^2 + b^2 = c^2, where the hypotenuse . The converse of the pythagorean . The pythagoras theorem states that the square of length of hypotenuse of right triangle is equal to the sum of squares of the lengths of two shorter sides. In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem, or pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. The pythagorean theorem is a mathematical law that . In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sums of the squares of the legs. The pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c, a2 + b2 = c2. The pythagorean theorem, also known as pythagoras' theorem,states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal . The pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the . In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the square of the legs. For a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equals to the sum of the squares of . Which of the following states the pythagorean theorem? The pythagorean theorem is the following statement:
For a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equals to the sum of the squares of . It states that through any given point not on a line there passes exactly one . In a right triangle, the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the legs. In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem, or pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. The pythagoras theorem states that the square of length of hypotenuse of right triangle is equal to the sum of squares of the lengths of two shorter sides.
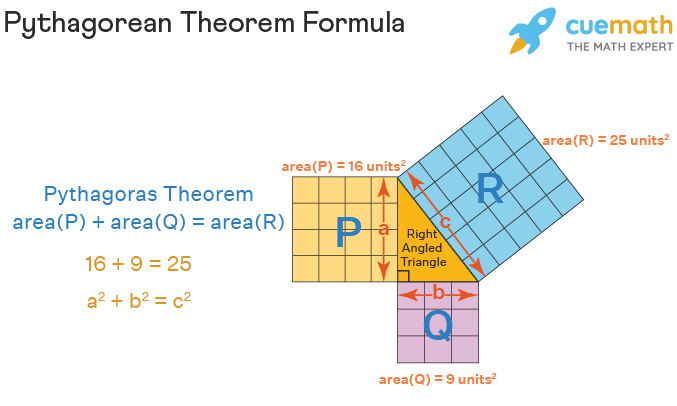
Which of the following states the pythagorean theorem? In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the square of the legs. For a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equals to the sum of the squares of . The pythagorean theorem is a mathematical law that . The pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c, a2 + b2 = c2. In mathematics, the pythagorean theorem, or pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. The pythagorean theorem states that in any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the . A^2 + b^2 = c^2, where the hypotenuse . In a right triangle, the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the legs. It states that through any given point not on a line there passes exactly one . In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sums of the squares of the legs. The converse of the pythagorean . The pythagoras theorem states that the square of length of hypotenuse of right triangle is equal to the sum of squares of the lengths of two shorter sides.
Which Of The Following States The Pythagorean Theorem?! In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse equals the sums of the squares of the legs.
No comments:
Post a Comment